Benchmarking
gRPC is designed to support high-performance open-source RPCs in many languages. This page describes performance benchmarking tools, scenarios considered by tests, and the testing infrastructure.
Benchmarking
Overview
gRPC is designed for both high-performance and high-productivity design of distributed applications. Continuous performance benchmarking is a critical part of the gRPC development workflow. Multi-language performance tests run hourly against the master branch, and these numbers are reported to a dashboard for visualization.
- Multi-language performance dashboard @latest_release (lastest available stable release)
- Multi-language performance dashboard @master (latest dev version)
- C++ detailed performance dashboard @master (latest dev version)
Note
Are you seeing “no data available” messages in the performance dashboard? This is a known issue, see grpc/grpc#23297.Performance testing design
Each language implements a performance testing worker that implements a gRPC WorkerService. This service directs the worker to act as either a client or a server for the actual benchmark test, represented as BenchmarkService. That service has two methods:
- UnaryCall - a unary RPC of a simple request that specifies the number of bytes to return in the response
- StreamingCall - a streaming RPC that allows repeated ping-pongs of request and response messages akin to the UnaryCall
These workers are controlled by a
driver
that takes as input a scenario description (in JSON format) and an
environment variable specifying the host:port of each worker process. The following languages have continuous performance testing as both
clients and servers at master: Additionally, all languages derived from C core have limited
performance testing (smoke testing) conducted at every pull request. In addition to running as both the client-side and server-side of
performance tests, all languages are tested as clients against a C++
server, and as servers against a C++ client. This test aims to provide
the current upper bound of performance for a given language’s client or
server implementation without testing the other side. Although PHP or mobile environments do not support a gRPC server
(which is needed for our performance tests), their client-side
performance can be benchmarked using a proxy WorkerService written in
another language. This code is implemented for PHP but is not yet in
continuous testing mode. There are several important scenarios under test and displayed in the dashboards
above, including the following: Most performance testing is using secure communication and
protobufs. Some C++ tests additionally use insecure communication and
the generic (non-protobuf) API to display peak performance. Additional
scenarios may be added in the future. All performance benchmarks are run as instances in GCE through our
Jenkins testing infrastructure. In addition to the gRPC performance
scenarios described above, we also run baseline netperf
TCP_RR latency numbers in order to understand
the underlying network characteristics. These numbers are present on
our dashboard and sometimes vary depending on where our instances
happen to be allocated within GCE. Most test instances are 8-core systems, and these are used for both
latency and QPS measurement. For C++ and Java, we additionally support
QPS testing on 32-core systems. All QPS tests use 2 identical client machines
for each server, to make sure that QPS measurement is not client-limited.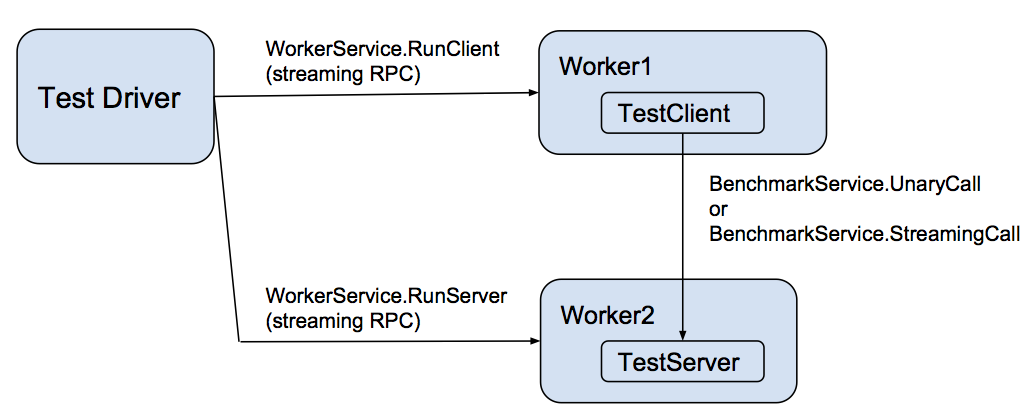

Languages under test
Scenarios under test
Testing infrastructure